
Stopping taking the pill is often a difficult experience, because it upsets your entire hormonal system, which has been on hiatus for some time. Your body has to readjust and learn to function on its own.
During this period and over the following 3 years, certain symptoms may appear and affect your well-being:
premenstrual pain, irregular cycles, acne, headaches, mood disorders, etc.
These symptoms that appear following the cessation of synthetic hormones are your body's way of showing that it needs help!
Pour préparer votre corps à l'arrêt de la pilule ou le rééquilibrer suite à un arrêt de contraception de moins de 3 ans, vous devez adapter votre hygiène de vie, c'est-à-dire ajuster l’ensemble de vos choix et de vos pratiques quotidiennes qui impactent votre santé et votre bien-être.
How does the pill work?
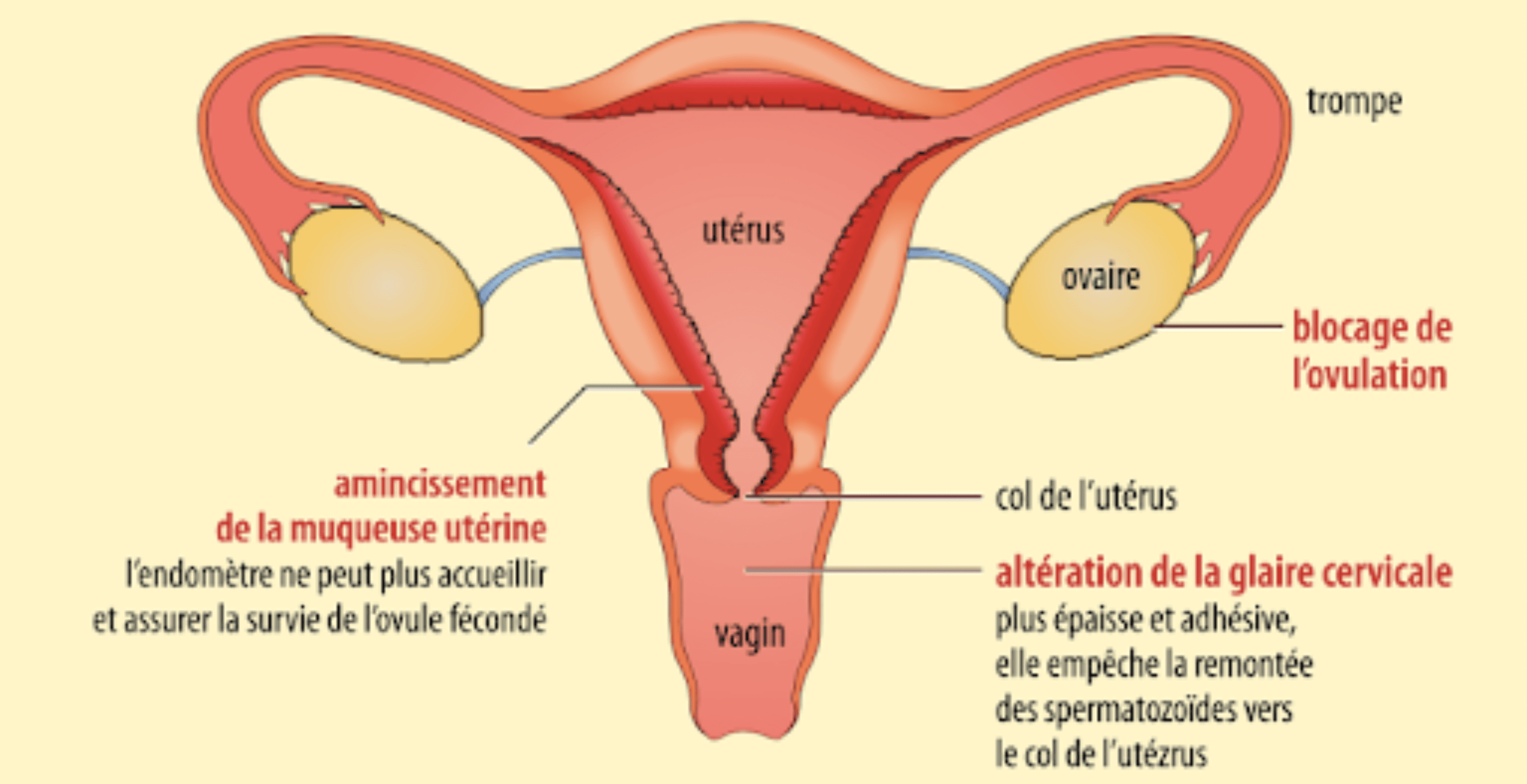
The pills release synthetic hormones that look like the ones your body makes naturally. These hormones will disrupt or even block your natural menstrual cycle.
There are two types of pills. The so-called "combined" or estrogen-progestin pills and the progestin-only pills.
Combination or estrogen-progestin pills contain two hormones: an estrogen and a progestin. By providing a constant dose of synthetic hormones, natural menstrual cycles are put to sleep.
This type of contraception has 3 mechanisms of action:
- Blocking ovulation in the ovaries:
Combination pills aim to reduce the concentration in the blood of the two hormones responsible for ovulation and produced in the pituitary gland: follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Blocking the way to sperm:
The progestin will thicken the cervical mucus at the cervix to make it impenetrable to spermatozoa
- Making implantation impossible:
The combined pill also acts on the uterine lining, preventing the possible implantation of an embryo.
Progestin-only pills are made up of a progestin-only hormone. These pills act on the thickness of the mucus at the level of the uterine cervix and, for some of them only, block ovulation. They are intended, for example, for women for whom the use of estrogen is contraindicated.
What happens in the body when you stop taking the pill?
If you are thinking about going off the pill or have already gone off the pill, you should know that this is the beginning of a process, which can take up to 3 years. After all, coming off the pill is a huge change for your hormonal balance. Your body needs some time to get used to the change in hormone production.
Stopping the pill will allow a return to the natural production of estrogen and progesterone. But beware of the rebound effect: if these hormones are produced in excess, you may see a number of symptoms appear:
Irregular periods:
For some women, this return to naturalness can take several months and modify their menstrual cycles which then become irregular.
Premenstrual syndrome:
After stopping the pill, symptoms of premenstrual syndrome may appear:
- Bloating
- Water Retention
- Tension of the breasts before the period
- Abdominal pain
- Irritability
- Nausea and vomiting
Bleeding between periods (metrorrhagia) and white discharge may also occur in the following months.
The change in libido:
The pill contains hormones that lower androgen levels, including testosterone, the desire hormone. When a woman's cycles are spontaneous again, her body is better prepared for sexual relations. Without the pill, libido is boosted, especially during the ovulatory period.
The return of acne:
When you take the pill, you artificially block the secretion of testosterone, which improves the condition of your acne and skin. This is why when you stop taking the pill, your skin returns to its natural state. If you had a tendency to have acne or oily skin before taking the pill, you can expect some pimples to reappear after stopping the pill.
The overworked liver:
When you have taken the pill for a long time, one of the most important victims is... your liver! In the body, the liver is responsible for filtering, neutralizing and eliminating toxins and synthetic molecules, including the hormones in the pill. All the toxins contained in the pill will overload the liver. It is the organ most affected with the years of taking the pill.
When you stop taking the pill, your hormonal system is out of balance and your liver is more overworked! It is therefore important to support the liver gently in its work.
Other effects:
Several symptoms can appear when you stop the pill, sometimes simultaneously, sometimes spaced out in time. These symptoms are not systematic and do not concern all women.
When you stop, the drop in hormone levels can also cause headaches, weight gain or hair loss. The quality of your hair may also be affected for a few months. Often, sebum production increases due to the hormonal turmoil, and the hair is more oily. Usually, the scalp change does not last more than three months.

Discover our e-book :
"How to better support our bodies before and after we stop taking the pill".

How can side effects be minimized through diet?
Stopping the pill is a key moment during which your body will have special needs to regain its balance.
Here are our tips for minimizing side effects:
- Give your body all the nutrients it needs. When you stop taking the pill, your body needs important resources to regain its hormonal balance. It is important to eat enough, in a varied and structured way (proteins, carbohydrates and fats) to provide all the elements your body needs on a daily basis. Fill up on good fats, vitamins and minerals.
- Reduce the toxic load as much as possible: avoid eating industrial and processed products (ready meals, cold cuts, etc.), food additives, and all foods rich in sugars and processed fatty acids.
- Take care of your liver, which is responsible for neutralizing spent estrogen. Your liver likes vegetables rich in chlorophyll (dark green in color) and sulfur (cabbage, broccoli). These foods participate in cell regeneration and help eliminate toxins and limit hormonal excess. You can also help your liver with appropriate plants: milk thistle, artichoke, black radish, or dandelion. .... Drinking a lot of water will also allow the liver and the whole system of elimination of waste, to eliminate toxins well.
- Promote your intestinal transit: Constipation is the number one enemy of your feminine balance. You can make a cure of probiotics during three months to restore your intestinal balance and renew 2 times per year, according to your needs.
Holistic food supplements
Composed of vitamins, minerals, trace elements and plant extracts, food supplements are a natural and effective way to rebalance the body after stopping the pill. They act directly at the heart of the cells and provide the micronutrients needed to reduce post-pill symptoms.
To allow women to live serenely the stop of their hormonal contraception, or for those who have already stopped it, D-LAB has developed the Post-Pill Detox, imagined in collaboration with Amal Tahir, coach, writer, specialized in positive sexuality. A 100% vegan formula that supports the female hormonal system as well as the emunctory organs involved in the detoxification process, to prepare the body for stopping the pill but also to accompany women who have already stopped the pill in the last 3 years and thus avoid the related symptoms.
1 - Restores hormonal balance
The Post-Pill Detox helps to restore hormonal balance in order to relieve the symptoms associated with stopping the pill: premenstrual pain, irregular cycles, headaches, mood disorders, etc.
- Vitamin B6 regulates hormonal activity by allowing the maintenance of normal levels of oestrogen and progesterone. It acts on symptoms such as anxiety, irritability and premenstrual nervous tension.
- Evening primrose oil, composed of gamma-linolenic and linoleic acids, helps to regulate the hormonal system, maintain optimum comfort during menstruation and helps to combat menstrual pain and hot flushes.
- Rose centifolia supports the function of the sexual organs and helps to maintain a comfortable menstrual cycle. It helps to alleviate premenstrual syndrome, cramps and bad moods.
2 - Preserves the health of the skin
The Post-Pill Detox contains herbal medicines, vitamins and minerals essential for healthy skin to avoid those common skin problems and post-pill skin sensitivity.
- Zinc is an essential trace element for the skin and is beneficial in reducing blemishes. It regulates the production of sebum and thus prevents the pores from becoming clogged and allows the skin to breathe. Zinc also promotes the regeneration of skin cells and combats the effects of cell ageing.
- Lodhra has effective astringent properties against acne. It helps to keep the skin healthy and improves the complexion.
3 - Detoxifies the body
The Post-Pill Detox protects and supports the health of the liver to promote elimination and purification of the body.
- Milk Thistle contains silymarin, a highly effective hepatoprotective active ingredient. It purifies the body in depth, eliminates toxins present in the liver and promotes rapid regeneration of damaged tissue.
- Burdock is a depurative plant known to promote the elimination of toxins and the purification of the blood.

What are the other methods of contraception?
Although the contraceptive pill remains the most widely used method of contraception in France, it is far from being the only one. Today, more and more women are deciding to switch to hormone-free contraception.
If you are tired of taking the pill every day or have trouble with its side effects, hormone-free birth control may be a solution.
The condom
The male condom is one of the most widely used hormone-free methods of contraception. Made of latex or polyurethane, it not only prevents sperm from passing through, but is also the only way to prevent the transmission of STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
There are also female condoms that are placed in the vagina before intercourse. It has a ring at each end of the condom to hold it in place and prevent it from being pulled into the vagina.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 98% - In typical use: 85
The IUD or IUD without hormones
The IUD (intrauterine device) is the most commonly recommended hormone-free contraceptive. It is also a very reliable contraceptive that you can wear for 5 to 10 years.
How does it work? The IUD consists of a thin copper wire that releases copper ions. These ions cause an inflammatory response in the walls of the uterus (endometrium) that creates an inhospitable environment for sperm and prevents the egg from attaching, even if it is fertilized.
However, this method of contraception causes some undesirable effects in some women such as heavier periods and pain.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 99.4% - In typical use: 99.2
Diaphragm and cervical cap
Diaphragms and cervical caps are non-hormonal contraceptives for women that are used with spermicides at the time of intercourse.
It is a latex or silicone membrane that you place in the vagina near the cervix just before intercourse. These devices block the passage of sperm. They must remain in place for at least 6 hours after intercourse.
They are used only during intercourse and should be removed afterwards, at least 6 to 8 hours after intercourse.
Both of these devices are available by prescription only. You should seek the advice of your gynecologist or midwife before using it.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 84% - In typical use: 83
Cycle Observation Methods (COM)
MOC requires monitoring fertility indicators (such as cervical mucus, temperature changes, or cervical position) and using extra protection on fertile days.
This natural contraceptive method is called "symptothermy": it mainly combines two fertility indicators:
1 - Observation of the cervical mucus :
As ovulation approaches, cervical mucus becomes more abundant, fluid and stringy. At the time of ovulation, the mucus takes on the consistency of egg white.
On the other hand, during non-fertile days, the cervical mucus is generally drier and less easy to observe.
2 - Temperature observation
After ovulation, the body temperature increases. This can easily be measured in the morning with a thermometer.
By taking daily fertility readings and plotting them on a graph called a "cyclogram", you will be able to define your fertility window for the current cycle.
During your fertile period, you have two options:
- You can protect yourself with mechanical contraception (condom, diaphragm, cervical cap, etc.). The failure rate is 1.8%.
- You and your partner can choose abstinence or sex without penetration. Here, the failure rate will be around 0.5%.





